Inverse Transform Sampling
逆变换采样(Inverse Transform Sampling or Inversion Method)是一种从标准均匀分布的随机数出发,通过变换生成按我们指定的概率密度分布的随机数的方法。[1][2]
问题
已知:随机变量\(X\)满足标准均匀分布,即\(X\sim U[0,1]\),然后要求生成随机变量\(Y\),使得\(Y\)满足概率密度分布\(f(y)\),其中\(f(y)\)对应的累积分布函数\(F(y)\)是严格单调增的。
方法
- 生成标准均匀分布的随机数\(X\)
- 计算累积分布函数的反函数\(F^{-1}(y)\)
- 带入反函数生成随机变量\(Y=F^{-1}(X)\),则\(Y\)满足概率密度分布\(f(y)\)
证明
对于随机变量\(X\),如果满足标准均匀分布的话,对任给的\(a\in[0, 1]\),有\(Pr(X≤a)=a\),那么有:
\[Pr(X≤F(y))=F(y)\]然后\(F(y)\)是值域\([0,1]\)上的严格单调递增函数,它一定存在反函数,且反函数也是严格单调递增的,于是:
\[Pr(F^{-1}(X)≤y)=F(y)\]根据累积分布函数的定义\(F(y) = Pr(X≤y)\),上式表明\(F^{-1}(X)\)是个满足累积分布函数\(F(y)\)的随机数,证毕。
例子
从标准均匀分布随机数生成满足指数分布的随机数,指数分布 \(X\sim exp(1)\)
\[f(x)=\begin{cases}e^{-x} & x\geq0 \\0 & x<0 \end{cases}\]-
累积分布函数: \(F(x)=\begin{cases}1-e^{-x} & x\geq0 \\0 & x<0 \end{cases}\)
- \(F(x)\)的反函数:\(F^{-1}(x)=-ln(1-x)\),其中\(x\in[0,1)\)
- \(X\)满足\(U[0,1]\)分布,则\(-ln(1-X)\)满足指数分布。
python代码:
import math
import random
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
N = 200000
Q = 20
S = 10
rand_counts = [0] * Q * S # random value counter, the counter proportion is the pdf(probability distribution function)
for i in range(N):
r = random.uniform(0, 1) # gen uniform random in range(0, 1)
r = -math.log(1 - r) # inverse transform to get exp distribution
c = (int)(r * S)
if c < Q * S:
rand_counts[c] = rand_counts[c] + 1
total = sum(rand_counts)
print ("total = ", total)
x = [0] * Q * S
y = [0] * Q * S
for i in range(Q * S):
x[i] = i / S
y[i] = rand_counts[i] * S / total
plt.plot(x,y)
plt.show()
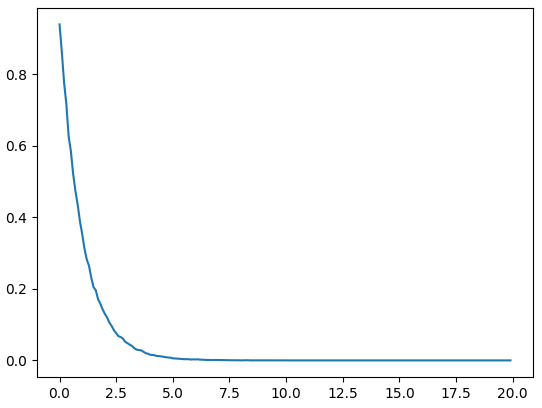
基本符合\(y=e^{-x}\)
Reference
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Inverse_transform_sampling
- https://dk81.github.io/dkmathstats_site/prob-inverse-cdf.html
- https://blogs.sas.com/content/iml/2013/07/22/the-inverse-cdf-method.html
- https://www.pbr-book.org/3ed-2018/Monte_Carlo_Integration/Sampling_Random_Variables
- http://corysimon.github.io/articles/uniformdistn-on-sphere/